Metals: Physical properties of metals, chemical properties of metals and non-metal oxide.
Metals are the elements that conduct heat and electricity and are malleable and ductile. Examples are Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Platinum (Pt), Lead (Pb), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) etc.
Metals are the elements which form positive ions by losing electrons. Thus, metals are known as Electropositive Elements.
Physical Properties of Metals
- Hardness: Most of the metals are hard, except alkali metals, such as sodium, potassium, lithium, etc. are very soft metals. These can be cut by using a knife.
- Strength: Most of the metals are strong and have high tensile strength. Because of this, big structures are made using metals, such as copper (Cu) and iron (Fe). (Except Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) which are soft metals).
- State: Metals are solid at room temperature except for mercury (Hg).
- Sound: Metals produce ringing sound, so, metals are called Sonorous. Sound of metals is also known as Metallic sound. This is the cause that metal wires are used in making musical instruments.
- Conduction: Metals are a good conductor of heat and electricity. This is the cause that electric wires are made of metals like copper and aluminium.
- Malleability: Metals are malleable. This means metals can be beaten into a thin sheet. Because of this property, iron is used in making big ships.
- Ductility: Metals are ductile. This means metals can be drawn into thin wire. Because of this property, a wire is made of metals.
- Melting and Boiling Point: Metals have generally high melting and boiling points. (Except sodium and potassium metals which have low melting and boiling point.)
- Density: Most of the metals have a high density.
- Colour: Most of the metals are grey in colour. But gold and copper are exceptions.
Chemical Properties of Metals
1. Reaction with oxygen: Most of the metals form respective metal oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Examples:
Reaction of Potassium with Oxygen: Potassium metal forms potassium oxide when reacts with oxygen.
Reaction of Sodium with Oxygen: Sodium metal forms sodium oxide when reacts with oxygen.
Lithium, potassium, sodium, etc. are known as Alkali-metals. Alkali metals react vigorously with oxygen.
Reaction of Copper metal with Oxygen: Copper does not react with oxygen at room temperature but when burnt in air, it gives oxide.
Silver, gold and platinum do not combine with the oxygen of air even at high temperature. They are the least reactive.
2. Reaction of metals with water: Metals form respective hydroxide and hydrogen gas when reacting with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
Most of the metals do not react with water. However, alkali metals react vigorously with water.
Reaction of Sodium metal with Water: Sodium metal forms sodium hydroxide and liberates hydrogen gas along with lot of heat when reacting with water.
Reaction of Calcium metal with Water: Calcium forms calcium hydroxide along with hydrogen gas and heat when react with water.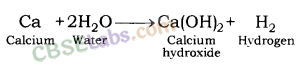
Reaction of Magnesium metal with Water: Magnesium metal reacts with water slowly and forms magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.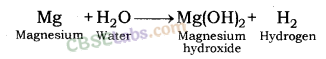
When steam is passed over magnesium metal, magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas are formed.
Reaction of Aluminium metal with Water: Reaction of aluminium metal with cold water is too slow to come into notice. But when steam is passed over aluminium metal, aluminium oxide and hydrogen gas are produced.
2Al + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 2H2
Reaction of Zinc metal with Water: Zinc metal produces zinc oxide and hydrogen gas when steam is passed over it. Zinc does not react with cold water.
Reaction of Iron with Water: Reaction of iron with cold water is very slow and comes into notice after a long time. Iron forms rust (iron oxide) when reacts with moisture present in the atmosphere. Iron oxide and hydrogen gas are formed by passing of steam over iron metal.
Both calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) are heavier than water but still float over it: Both calcium and magnesium float over water surface because hydrogen gas is evolved when these metals react with water. It is in the form of bubbles which stick on the metal surface. Therefore, they float over it.
Other metals usually do not react with water or react very slowly. Lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with steam. Thus, the order of reactivity of different metals towards water may be written as :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Ae > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag > Au
3. Reaction of metals with dilute acid: Metals form respective salts when reacting with dilute acid.
Metal + dil. acid → Metal salt + Hydrogen
Reaction of Sodium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Sodium metal gives sodium chloride and hydrogen gas when react with dilute hydrochloric acid.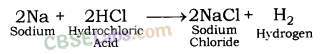
Reaction of Magnesium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed when magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reaction of Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid: Zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed when zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid. This method is used in the laboratory to produce hydrogen gas.
Hydrogen (H2) gas is not evolved when metal is treated with nitric acid (HNO3):
Nitric acid is strong oxidising agent and it oxidises the hydrogen gas (H2) liberated into water (H2O) and itself get reduced to some oxide of nitrogen like nitrous oxide (N2O)3 nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Copper, gold, silver are known as noble metals. These do not react with water or dilute acids.
The order of reactivity of metal towards dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid is in the order;
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Hg > Ag
Metal Oxides
Chemical Properties: Metal oxides are basic in nature. The aqueous solution of metal oxides turns red litmus blue.
Reaction of Metal oxides with Water: Most of the metal oxides are insoluble in water. Alkali metal oxides are soluble in water. Alkali metal oxides give strong base when dissolved in water.
Reaction of Sodium oxide with Water: Sodium oxide gives sodium hydroxide when reacts with water.
Reaction of Potassium oxide with Water: Potassium oxide gives potassium hydroxide when reacts with water.
Reaction of Zinc oxide and Aluminium oxide: Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are insoluble in water. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature. An amphoteric substance shows both acidic and basic characters. It reacts with base like acid and reacts with an acid like a base.
When zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it behaves like an acid. In this reaction, sodium zincate and water are formed.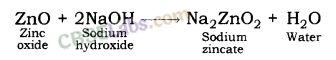
Zinc oxide behaves like a base when reacts with acid. Zinc oxide gives zinc chloride and water on reaction with hydrochloric acid.
In a similar way, aluminium oxide behaves like a base when reacts with acid and behaves like acid when reacts with a base.
Aluminium oxide gives sodium aluminate along with water when reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Aluminium oxide gives aluminium chloride along with water when it reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Reactivity Series of Metals: The order of intensity or reactivity of metal is known as Reactivity Series. Reactivity of elements decreases on moving from top to bottom in the given reactivity series.
In the reactivity series, copper, gold, and silver are at the bottom and hence, least reactive. These metals are known as Noble metals. Potassium is at the top of the series and hence, most reactive.
Reactivity of some metals are given in descending order :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
4. Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts: Reaction of metals with the solution of other metal salt is displacement reaction. In this reaction, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt.
Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Examples :
Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
Similarly, aluminium and zinc displace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.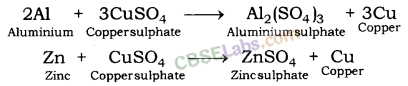
In all the above examples, iron, aluminium and zinc are more reactive than copper. This is why they displace copper from its salt solution.
When copper is dipped in the solution of silver nitrate, it displaces silver and forms copper nitrate.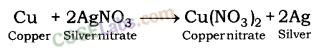
In the reaction, copper is more reactive than silver and hence, displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
Silver metal does not react with copper sulphate solution because silver is less reactive than copper and not able to displace copper from its salt solution.
Similarly, when gold is dipped in the solution of copper nitrate, no reaction takes place because copper is more reactive than gold.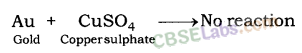
In similar way, no reaction takes place when copper is dipped in the solution of aluminium nitrate because copper is less reactive than aluminium.
Non-Metals: Physical Properties of non-metals, chemical properties of non-metals, non¬metal oxides, Reaction of metal and Non-metal, Ionic bonds and formation of an ionic bond. Non-metals are the elements that do not conduct electricity and are neither malleable nor ductile.
Examples: Carbon (C), Sulphur (S), Phosphorous (P), Silicon (Si), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Neon (Ne) and Argon (Ar) etc.
Non-metals are the elements which form negative ions by gaining an electron. Thus, non¬metals are also known as Electronegative Elements.
Physical properties of non-metals
- Hardness: Non-metals are not hard rather they are generally soft. But the diamond is an exception; it is the hardest naturally occurring substance.
- State: Non-metals may be solid, liquid or gas.
- Lustre: Non-metals have a dull appearance. Diamond and iodine are exceptions.
- Sonority: Non-metals are not sonorous, i.e., they do not produce a typical sound on being hit.
- Conduction: Non-metals are a bad conductor of heat and electricity. Graphite which is allotrope of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exception.
- Malleability and ductility: Non-metals are brittle.
- Melting and boiling point: Non-metals have generally low melting and boiling points.
- Density: Most of the non-metals have low density.
- Colour: Non-metals are in many colours.
Carbon in the form of graphite is non-metal which conduct electricity.
Iodine is non-metal which is lustrous having a shining surface.
Carbon in the form of diamond is a non-metal which is extremely hard.
Diamond is a non-metal which has a very high melting point and boiling point.
Chemical properties of Non-metals
1. Reaction of Non-metals with Oxygen: Non-metals form respective oxide when reacting with oxygen.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metallic oxide
When carbon reacts with oxygen, carbon dioxide is formed along with the production of heat.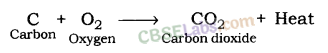
When carbon is burnt in an insufficient supply of air, it forms carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is a toxic substance. Inhaling of carbon monoxide may prove fatal.![]()
Sulphur gives sulphur dioxide when reacting with oxygen. Sulphur catches fire when exposed to air.![]()
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen it gives water.![]()
Non-metallic Oxide: Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. The solution of non-metal oxides turns blue litmus red.
Carbon dioxide gives carbonic acid when dissolved in water.![]()
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphurous acid when dissolved in water.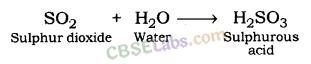
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphuric acid when reacts with oxygen.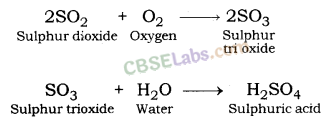
2. Reaction of Non-metal with Chlorine: Non-metal gives respective chloride when they react with chlorine gas.
Non-metal + Chlorine → Non-metal chloride
Hydrogen gives hydrogen chloride and phosphorous gives phosphorous trichloride when reacting with chlorine.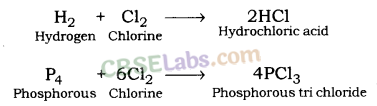
3. Reaction of Non-metals with Hydrogen: Non-metals reactive with hydrogen to form covalent hydrides.
Non-metal + Hydrogen → Covalent Hydride
Sulphur combines with hydrogen to form a covalent hydride is called Hydrogen sulphide.
Nitrogen combines with hydrogen in presence of an iron catalyst to form covalent hydride ammonia.
Non-metals do not react with water (or steam) to evolve Hydrogen gas.
Non-metals do not react with dilute acids.
4. Reaction of Metal and Non-metal: Many metals form ionic bonds when they react with non-metals. Compounds so formed are known as Ionic Compounds.
Ions: Positive or negative charged atoms are known as ions. Ions are formed because of loss or gain of electrons. Atoms form ions obtain by the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas.
Positive ion: A positive ion is formed because of the loss of electrons by an atom.
Following are some examples of positive ions:
Sodium forms sodium ion because of the loss of one electron. Because of the loss of one electron, one positive charge comes over sodium.![]()
Magnesium forms positive ion because of the loss of two electrons. Two positive charges come over magnesium because of loss of two electrons.
Negative ion: A negative ion is formed because of the gain of an electron.
Some examples are given below :
Chlorine gains one electron in order to achieve a stable configuration. After the loss of one electron, chlorine gets one negative charge over it forming chlorine ion.
Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are formed because of transfer of electrons from metal to non¬metal. In this course, metals get positive charge because of transfer of electrons and non-metal gets negative charge because of acceptance of electrons. In other words, bond formed between positive and negative ion is called Ionic Bond.
Since, a compound is electrically neutral, so to form an ionic compound, negative and positive both ions must be combined.
Some examples are given below:
Formation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl): In sodium chloride, sodium is a metal (alkali metal) and chlorine is a non-metal.
Atomic number of sodium = 11
Electronic configuration of sodium : 2, 8, 1
Number of electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Valence electrons = Electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Atomic number of chlorine = 17
Electronic configuration of chlorine : 2, 8, 7
Electrons in outermost orbit = 7
Therefore, valence electrons = ?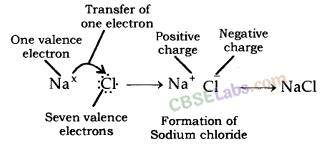
Sodium has one valence electron and chlorine has seven valence electrons. Sodium requires losing one electron to obtain stable configuration and chlorine requires gaining one electron in order to obtain stable electronic configuration. Thus, in order to obtain stable configuration, sodium transfers one electron to chlorine. After loss of one electron, sodium gets one positive charge (+) and chlorine gets one negative charge after gain of one electron. Sodium chloride is formed because of transfer of electrons. Thus, ionic bond is formed between sodium and chlorine. Since, sodium chloride is formed because of ionic bond, thus, it is called Ionic compound. In similar way, potassium chloride (KCl) is formed.
Properties of Ionic compound
- Ionic compounds are solid. Ionic bond has a greater force of attraction because of which ions attract each other strongly. This makes ionic compounds solid.
- Ionic compounds are brittle.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because force of attraction between ions of ionic compounds is very strong.
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve in water.
- Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in organic solvents; like kerosene, petrol, etc.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
- The solution of ionic compounds in water conduct electricity. This happens because ions present in the solution of ionic compound facilitate the passage of electricity by moving towards opposite electrodes.
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals: Minerals, ores, extraction of metals of least reactivity, extraction of metals of middle reactivity, extraction of metals of high reactivity, refining or purification of metals and corrosion.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals:
Source of metal: Metals occur in Earth’s crust and in seawater; in the form of ores. Earth’s crust is the major source of metal. Seawater contains many salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc.
Mineral: Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have a uniform composition.
Ores: The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called Ores.
Metals found at the bottom of reactivity series are least reactive and they are often found in nature in free-state; such as gold, silver, copper, etc. Copper and silver are also found in the form of sulphide and oxide ores.
Metals found in the middle of reactivity series, such as Zn, Fe, Pb, etc. are usually found in the form of oxides, sulphides or carbonates.
Metals found at the top of the reactivity series are never found in free-state as they are very reactive, example; K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al, etc.
Many metals are found in the form of oxides because oxygen is abundant in nature and is very reactive.
Extraction of Metals: Metals can be categorised into three parts on the basis of their reactivity: Most reactive, medium reactive and least reactive.
The three major steps involved in the extraction of a metal from its ore are
- Concentration or enrichment of ores.
- Conversion of concentrated ore into crude metal and,
- Refining of impure or crude metal.
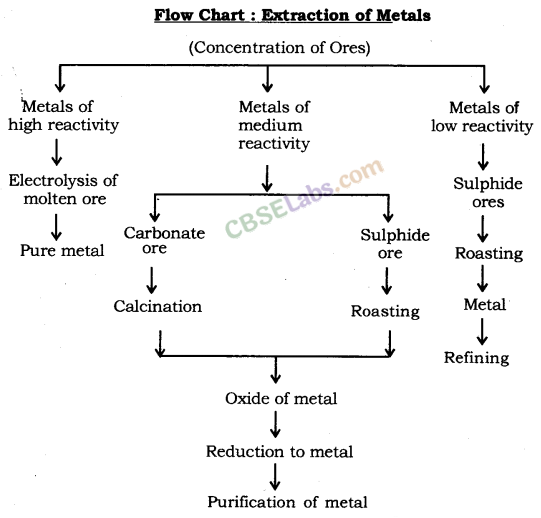
1. Concentration of Ores: Removal of impurities, such as soil, sand, stone, silicates, etc. from mines ore is known as Concentration of Ores.
Ores which are mined often contain many impurities. These impurities are called gangue. First of all, concentration is done to remove impurities from ores. The concentration of ores is also known as enrichment of ores. Process of concentration depends upon physical and chemical properties of ores. Gravity separation, electromagnetic separation, froth flotation process, etc. are some examples of the processes which are applied for concentration of ores.
2. Conversion of Concentrated Ore into Crude Metal
Conversion of metals ores into oxides: It is easy to obtain metals from their oxides. So, ores found in the form of sulphide and carbonates are first converted to their oxides by the process of roasting and calcination. Oxides of metals so obtained are converted into metals by the process of reduction.
Roasting: Heating of sulphide ores in the presence of excess air to convert them into oxides is known as Roasting.![]()
Calcination: Heating of carbonate ores in the limited supply of air to convert them into oxides is known as Calcination.![]()
| Calcination | Roasting |
| (i) It is done for carbonate ores. | (i) It is done for sulphide ores. |
| (ii) Carbonates ores heated in the absence of oxygen. | (ii) Sulphide ores are heated in the Presence of oxygen. |
| (iii) The CO2 gas is released and Metal oxide is obtained. ZnCO3(s) | (iii) SO2 gas is released and Metal oxide is obtained. 2ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) |
3. Reduction: Heating of oxides of metals to turn them into metal is known as Reduction.
(i) Extraction of Metals of Least Reactivity: Mercury and copper, which belong to the least reactivity series, are often found in the form of their sulphide ores. Cinnabar (HgS) is the ore of mercury. Copper glance (Cu2S) is the ore of copper.
Extraction of Mercury Metal: Cinnabar (HgS) is first heated in air. This turns HgS (mercury sulphide or cinnabar) into HgO (mercury oxide) by liberation of sulphur dioxide. Mercury oxide so obtained is again heated strongly. This reduces mercury oxide to mercury metal.
Extraction of Copper Metal: Copper glance (Cu2S) is roasted in the presence of air. Roasting turns copper glance (ore of copper) into copper (l) oxide. Copper oxide is then heated in the absence of air. This reduces copper (l) oxide into copper metal.
(ii) Extraction of Metals of Middle Reactivity: Iron, zinc, lead, etc. are found in the form of carbonate or sulphide ores. Carbonate or sulphide ores of metals are first converted into respective oxides and then oxides are reduced to respective metals.
Extraction of Zinc: Zinc blende (ZnS: zinc sulphide) and smithsonite or zinc spar or calamine (ZnCO3: zinc carbonate) are ores of zinc. Zinc blende is roasted to be converted into zinc oxide. Zinc spar is put under calcination to be converted into zinc oxide.
Zinc oxide so obtained is reduced to zinc metal by heating with carbon (a reducing agent).
Extraction of Iron from Haematite (Fe2O3): Haematite ore is heated with carbon to be reduced to iron metal.
Extraction of Lead from Lead oxide: Lead oxide is heated with carbon to be reduced to lead metal.
Reduction of Metal oxide by Heating with Aluminium: Metal oxides are heated with aluminium (a reducing agent) to be reduced to metal. Following is an example: Manganese dioxide and copper oxide are reduced to respective metals when heated with aluminium.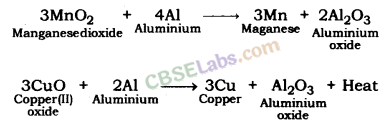
Thermite Reaction: Ferric oxide; when heated with aluminium; is reduced to iron metal. In this reaction, a lot of heat is produced. The thermite reaction is used in the welding of electric conductors, iron joints, etc. such as joints in railway tracks. This is also known as Thermite Welding (TW).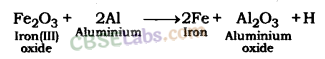
(iii) Extraction of Metals of High Reactivity: Metals of high reactivity; such as sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, etc. are extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction. These metals cannot be reduced using carbon because carbon is less reactive than them.
Electrolytic Reduction: Electric current is passed through the molten state of metal ores. Metal being positively charged is deposited over the cathode.
Example: When an electric current is passed through molten state or solution of sodium chloride, sodium metal gets deposited over the cathode.
Metals obtained from the process of electrolytic reduction are pure in form.
4. Refining or purification of metals: Metals extracted from various methods contains some impurities, thus, they are required to be refined. Most of the metals are refined using electrolytic refining.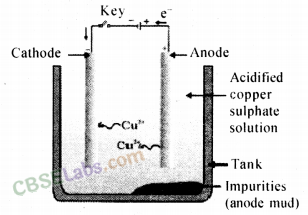
Electrolytic Refining: In the process of electrolytic refining, a lump of impure metal and a thin strip of pure metal are dipped in the salt solution of metal to be refined. When an electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal is deposited over a thin strip of pure metal
from a lump of impure metal. In this, impure metal is used as anode and pure metal is used as a cathode.
Electrolytic Refining of Copper: A lump of impure copper metal and a thin strip of pure copper are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate. Impure lump of metal is connected with the positive pole and thin strip of pure metal is connected with negative pole. When electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal from anode moves towards cathode and is deposited over it. Impurities present in metal are settled near the bottom of anode in the solution. Settled impurities in the solution are called Anode Mud.
5. Corrosion: Most of the metals keep on reacting with the atmospheric air. This leads to the formation of a layer over the metal. In the long run, the underlying layer of metal keeps on getting lost due to conversion into oxides or sulphides or carbonate, etc. As a result, the metal gets eaten up. The process is called Corrosion.
Rusting of Iron: Rusting of iron is the most common form of corrosion. When iron articles like the gate, grill, fencing, etc. come in contact with moisture present in the air, the upper layer of iron turns into iron oxide. Iron oxide is brown-red in colour and is known as Rust. The phenomenon is called Rusting of Iron.
If rusting is not prevented in time, the whole iron article would turn into iron oxide. This is also known as Corrosion of Iron. Rusting of iron gives a huge loss every year.
Prevention of Rusting: For rusting, iron must come in contact with oxygen and water. Rusting is prevented by preventing the reaction between atmospheric moisture and the iron article. This can be done by:
- Painting
- Greasing
- Galvanization
- Electroplating
- Alloying
6. Alloys: The homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal is called Alloy.
Types of alloys :
- Ferrous alloys: An alloy in which iron (Fe) is present. For example : manganese steel (Fe = 86% ; Mn = 13% ; C = 1%) and Nickle steel (Fe = 98% ; Ni = 2%).
- Non-ferrous alloys: An alloy does not contain iron. For example : Brass (Cu = 80% ; Zn = 20%), and Bronze (Cu = 90% ; Sn = 10%).
- Amalgams: An alloy in which mercury (Hg) is present. For example Sodium amalgams [Na(Hg)] and Zinc amalgams [Zn(Hg)].
Properties of an Alloy
- Alloys are stronger than the metal from which they are obtained.
- It is harder than the constituent metals.
- More resistance to corrosion.
- The melting point of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
Example: Solder [Sn(80%) + Pb(50%)] has lower m. p. than Pb and Sn. - The electrical conductivity of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
Some examples of Alloys:
- Brass: [80% Cu + 20% Zn ]
- Bronze: [90% Cu + 20% Sn]
- Solder: [50% Pb + 50% Sn]
- Duralumin: [95% Al + 4% Cu + 0.5% Mg + 0.5 Mn]
- Steel: [99.95% Fe + 0.05% C]
- Stainless steel: [74% Fe + 18% Cr + 8% Ni]
- Magnesium: [95% Al + 5% Mg]
- German Silver: [60% Cu + 20% Zn + 20% Ni]
- Alloys of Gold: Pure gold is said to be of 24 carats. Gold is alloyed with a small amount of silver or copper to make it hard.
Metals and Non-metals:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Metals generally occur as hard solid substances. | 1. Non-metals generally occur in all the three forms of matter- solid, liquid and gases. |
| 2. Metals are malleable and ductile. | 2. Non-metals are non-malleable and non-ductile. |
| 3. Metals produce ringing sound on striking which is called their sonorous property. | 3. Non-metals do not show this sonorous property. |
| 4. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. | 4. Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity with the exception of graphite which is a good conductor of heat and electricity. |
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals.
The reaction of metals with oxygen. Metals form their oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
Metal oxides are basic in nature. Example, Reaction of Iron metal with oxygen When iron reacts with moist air, it forms rust.
Rust is iron oxide. Articles made of iron, such as grills, fencing, etc. are getting rusted because of reaction with moist air.
Iron (Fe) + Water (H2O) + Oxygen (O2) → Fe3O4n.H2O (Iron II, III) Oxide (Rust)
Rust is reddish brown in colour and is iron oxide. Iron oxide is basic in nature. It turns red litmus blue.
Rusting of iron can be prevented:
- by galvanizing the iron articles with zinc coating.
- by painting and applying grease on the articles.
The reaction of Magnesium metal with oxygen: When magnesium is burnt in air, it forms magnesium oxide. Burning in the air means reaction with oxygen.
Magnesium + Oxygen (O2) → MgO (Magnesium oxide)
Magnesium oxide forms magnesium hydroxide with water. The solution of Magnesium oxide turns red litmus paper blue. This means magnesium oxide is basic in nature.
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2 (Magnesium Hydroxide)
The reaction of Non-metals with oxygen: Non-metals form their oxides when they react with oxygen.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metal oxide
Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature.
Example., Reaction of sulphur with oxygen.
When sulphur is burnt in air, it forms sulphur dioxide.
Sulphur + Oxygen (O2) → SO2 (Sulphur dioxide)
The solution of sulphur dioxide turns blue litmus paper red. Sulphur dioxide forms sulphurous acid when dissolved in water. Thus, sulphur dioxide is acidic in nature.
SO2 + H2O → Sulphurous acid (H2SO3)
The reaction of carbon with oxygen—When carbon is burnt in air, it forms carbon dioxide.
Carbon + Oxygen (O2) → CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
You can observe that when coal (carbon) is burnt it forms smoke, which contains carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is acidic in nature. The solution of carbon dioxide in water turns blue litmus paper red.
CO2 + H2O → Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
The reaction of Metals and Non-metals with water: Generally, metals form respective hydroxides when they react with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide
The reaction of sodium metal with water: Sodium metal vigorously reacts with water and forms sodium hydroxide along with a lot of heat.
Na + H2O → NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) + H2 (Hydrogen) + Heat
Non-metals generally do not react with water. Rather some non-metals which react with air vigorously are stored in water. The reaction of metals and non-metals with dilute acid. Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with dilute acid.
Metal + Acid → Hydrogen gas + Salt
The reaction of zinc with dilute acid. Zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc chloride when it reacts with hydrochloric acid. Similarly, zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc sulphate when it reacts with sulphuric acid. This method is used to produce hydrogen gas in the laboratory.
Zn + H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid) → ZnSO4 (Zinc sulphate) + H2 (Hydrogen)
The reaction of Aluminium with dilute acid. Aluminium gives hydrogen gas along with aluminium chloride when it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
2Al + 6HCl (Hydrochloric acid) → 2AlCl3 (Aluminium Chloride) + 3H2 (Hydrogen)
Copper does not react with dilute sulphuric acid even on heating, but it reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid. Copper, silver and gold are considered as noble metals as do not react with dilute acid.
Generally, non-metals do not react with dilute acid.
The reaction of metals and non-metals with the base. Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with a base.
Metal + Base → Hydrogen gas + Salt
The reaction of aluminium metal with sodium hydroxide.
Al + NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) → NaAlO2 (Sodium aluminate) + H2 (Hydrogen)
Aluminium metal forms hydrogen gas and sodium aluminate when it reacts with sodium hydroxide. Similarly, zinc gives sodium zincate and hydrogen gas when it reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Displacement Reaction: When a more reactive metal reacts with the salt solution of less reactive metal, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its solution.
Metal A + Salt Solution of metal B → Salt Solution of metal A + metal B
In the above equation, metal A is more reactive than metal B.
Example., When aluminium metal is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate, it forms aluminium sulphate and copper.
Al + CuSO4 (Copper sulphate) → Al2(SO4)3 (Aluminium Sulphate) + Cu (Copper)
In the above reaction, aluminium is more reactive than copper, that is why it replaces copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
When copper metal is dipped in the solution of aluminium nitrate, no reaction takes place. Because copper is less reactive than aluminium.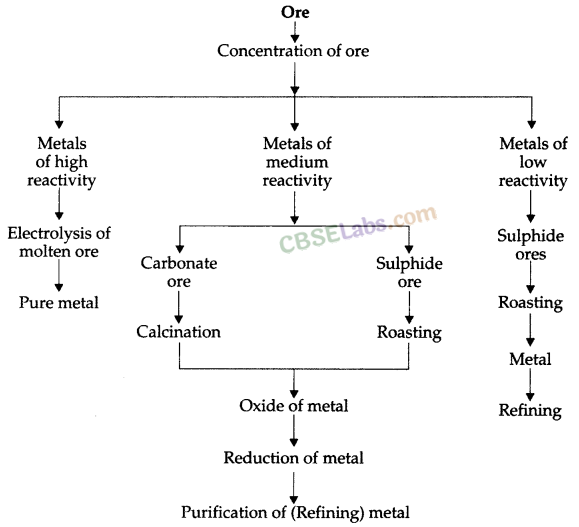
Roasting and Calcination:
| Roasting | Calcination |
| 1. It is done in case of sulphide ores. | 1. It is done in case of carbonate ores. |
| 2. In this, the ore is heated in the presence of air to convert it into oxide compound. | 2. The carbonate ore is heated in the absence of air to convert into oxide. |
| 3. The gas given out is SO2 (sulphur dioxide) gas. | 3. The gas given out is CO2 (carbon dioxide) gas. |
4. Example:  | 4. Example: |




0 Comments